
Aircrafts
AMERICAN AIRCRAFT OF WORLD WAR II
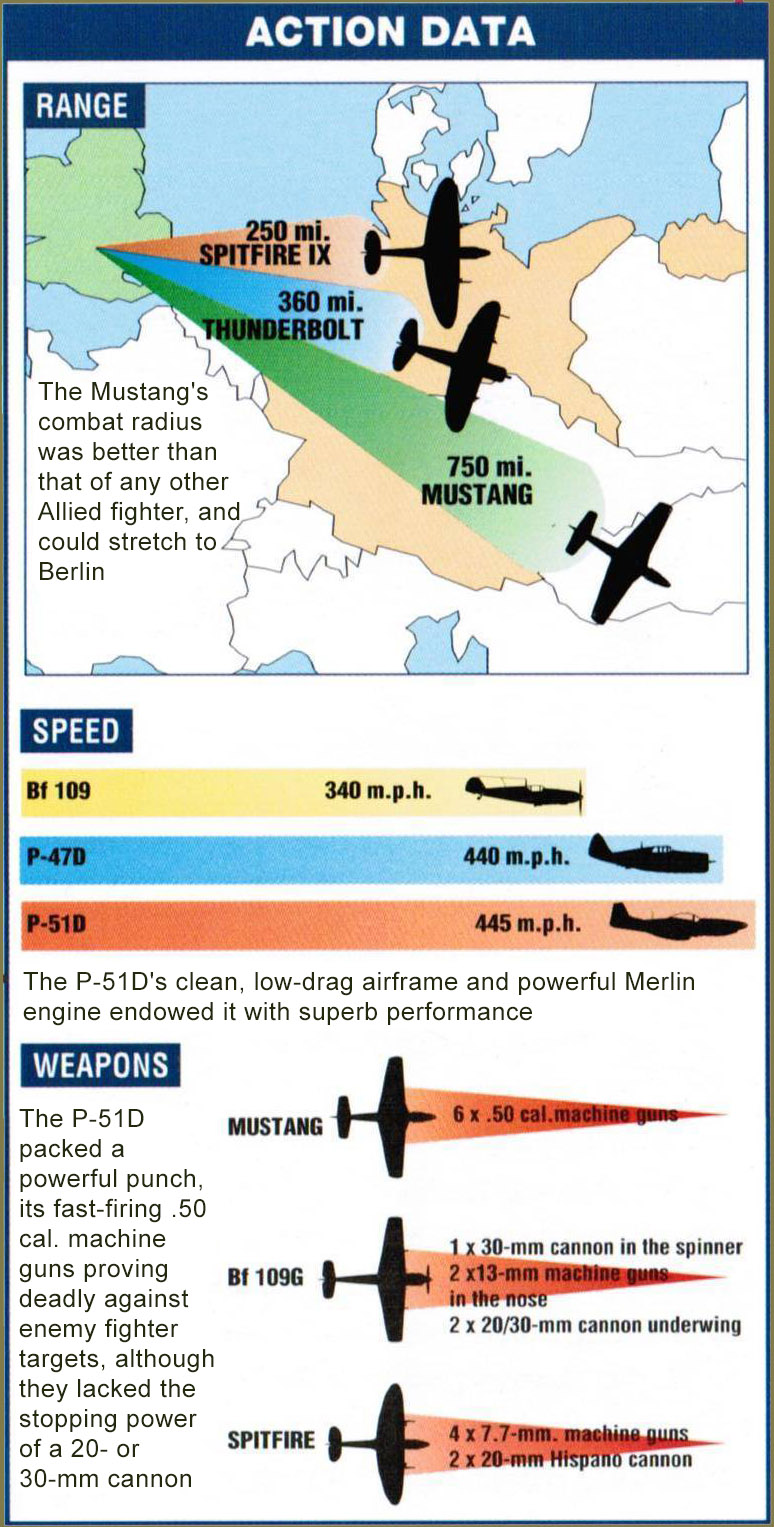
▶ Long-range escort fighter
▶ Most Allied kills
▶ 281 Mustang aces
As the bombers of the Eighth Air Force fought their way deep into Hitler's heartland, it was the Mustang that cleared the skies of Luftwaffe fighters. No other combat airplane of the war could fly as high, go as far and fight as hard as the mighty Mustang. In the skilled hands of young U.S. Air Corps pilots, it took on all comers and accounted for more kills than any other Allied airplane.

One of the great Mustang heroes, Major Don Gentile, with his favorite machine "Shangri-La" during 1943. He made 15 kills in Mustangs - half of them in one month.

Mustangs were flown by more aces than any other Allied fighter. Their prey even included the Me 262 jet.
Top Gun to the bomber force
Faced with invasion in 1939 and desperately short of lighters, the Royal Air Force asked North American Aviation to quickly produce the existing but obsolete P-40 Warhawk. Instead, the company designed, built and flew a new airplane in just 117 days - the Mustang.
Using an existing Allison engine and the latest laminar-flow wing, the new fighter immediately went into service with the RAF. In
December 1941 the United States joined the war, and it too needed good fighters fast. So the U.S. Air Corps took the basic RAF Mustang, rearmed it with four machine guns, and added an uprated engine. It was a good performer, but couldn't operate well alongside the high-flying long-range bomber.

By 1944 the aircraft used the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine, adopted a new bubble cockpit and increased its firepower to six .50 caliber machine guns. It was now the best fighter in the war and fought superbly in all theaters, as fighter, fighter-bomber and reconnaissance platform. It was loved by its aircrews, and no fewer than 281 Mustang pilots became aces - each shooting down at least five enemy aircraft.

P-51K Mustang "Nooky Booky IV"
This P-51K was flown by Major Leonard "Kit" Carson (left) of the 362nd Fighter Squadron, based at Leiston, England, as part of the 357th Fighter Group during 1944. Carson was one of the top-scoring Mustang aces, with 18 air-to-air victories.

SPECIFICATIONS P-51D Mustang
Type: Single-seat long-range escort fighter, fighter-bomber.
Powerplant: One 1,510-hp. Packard V-1650-7 (U.S.-built Rolls-Royce Merlin 61) inverted-vee 12-cylinder inline water-cooled piston engine.
Maximum speed: 445 m.p.h. at 25,000 ft.
Combat radius: 325 miles on internal fuel; 750 miles with two 130-gal. tanks.
Service ceiling: 41,900 ft.
Weapons: Six .50 cal. Browning machine guns in wings; two 500-lb. bombs or eight 75-mm rockets in place of long-range drop tanks.
Weights: Empty 7,125 lb.; Loaded 11,600 lb.
Dimensions: Span 37 ft.
Length 32 ft. 3 in.
Height 12 ft. 2 in.
Wing area 235 sq. ft.
Mustang, the all-the-way escort fighter

THE BOMBERS: Eighth Air Corps bombers left their British bases an hour ahead of the Mustangs, escorted in the first part of the mission by shorter-ranged P-38s and P-47s.

HAND OVER: The faster Mustangs would catch the formation over the Dutch/German border, where they would relieve the P-38s and Thunderbolts high above the B-17s.

ESCORT: Some fighters flew close escort. Their nearness boosted the morale of the bomber crews, who had been so severely mauled over Germany the year before.

DOGFIGHTER: The Mustang had more than long range. It was fast and it was a ferocious dogfighter, as the pilot of this Messerschmitt Bf 109G shot down by a P-51 discovered.

CONTROL OF THE SKIES: It was the appearance of swarms of these graceful fighters in the skies over Germany that was to signal the death knell of the Luftwaffe.
North American P-51D Mustang
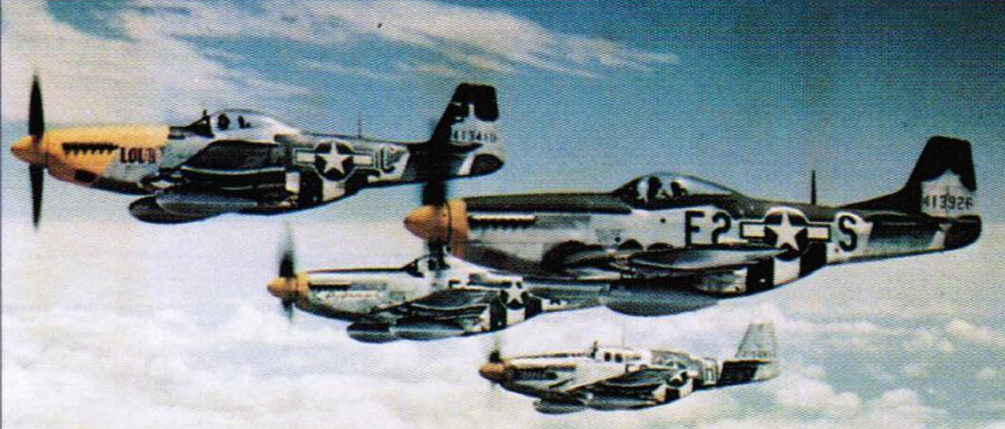

All the way
With underwing tanks, Mustangs had enough range to be able to escort their charges 1,700 miles to the target. When they got there, they were agile enough to beat all comers.
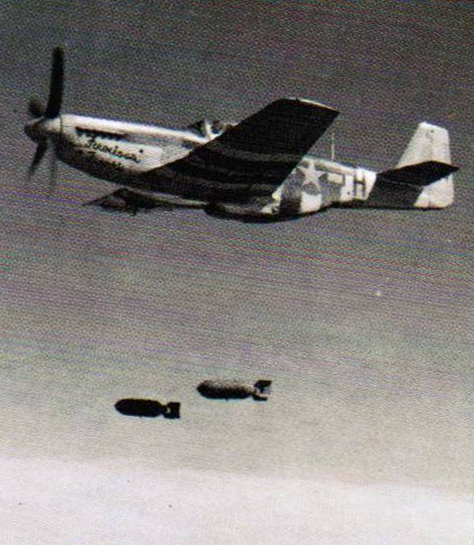

Mud movers
The Mustang's hard-hitting and accurate guns made it an excellent ground attack aircraft, that could also deliver air-to-ground rockets or bombs.
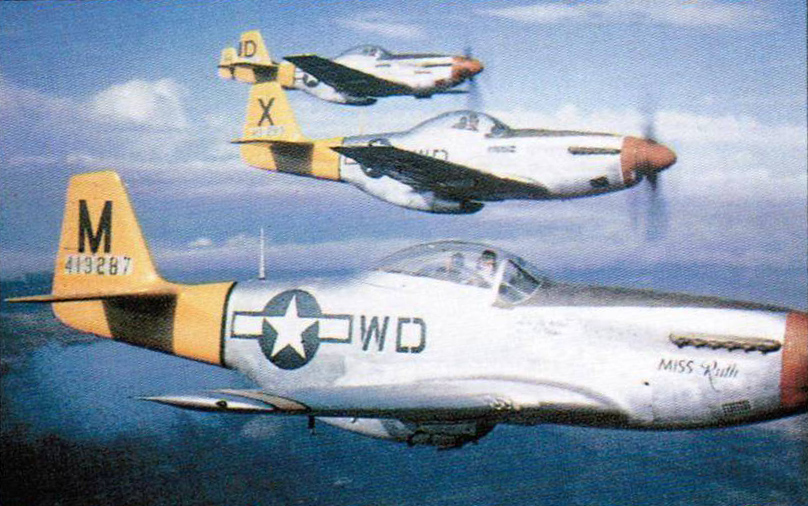

High flyer
The Mustang's phenomenal range and performance made it ideal for escorting high-flying B-29s across the vast Pacific.
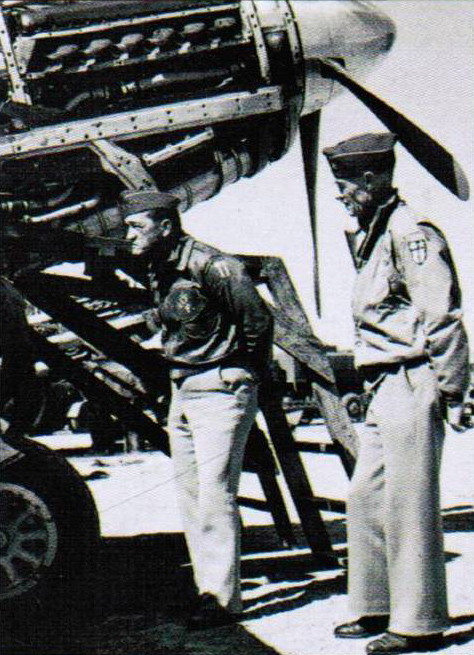

Powerpack
The early Mustang was transformed into a superb high-level fighter by the British-designed, Packard-built Rolls-Royce Merlin engine, which could deliver 1,510 horsepower.

Flying veterans
The Mustang's impeccable handling characteristics, bubble canopy and performance make it a popular rich man's toy - and many of them are still flying today. This example even carries a passenger.
FACTS AND FIGURES
▶ Ordered by the British, the prototype Mustang was proposed, designed, built and flown in an incredible 117 days.
▶ That initial aircraft was the first of 15,686 examples of the P-51 produced.
▶ The Mustang was flown by 11 Allied air forces in addition to the U.S. Air Corps.
▶ 281 Allied Mustang pilots qualified as "Aces," with five or more kills.
▶ The late-model P-51H was, at 472 m.p.h., one of the fastest piston-engine fighters.
▶ In October 1944, Mustang pilot Lieutenant Urban L. Drew managed the astonishing feat of shooting down two Me 262 jets.
AMERICAN AIRCRAFT OF WORLD WAR II
▶ Long-range heavy bomber
▶ Backbone of the U.S. Eighth Air Force
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress was one of the most important bombers in history. B-17s fought in every theater of World War II but won immortality in their epic daylight battles against the Luftwaffe. Thousands of young German and American fliers lost their lives, transforming the impotent United States Army Air Force of early 1943 into a force of devastating, destructive power in just 12 months.
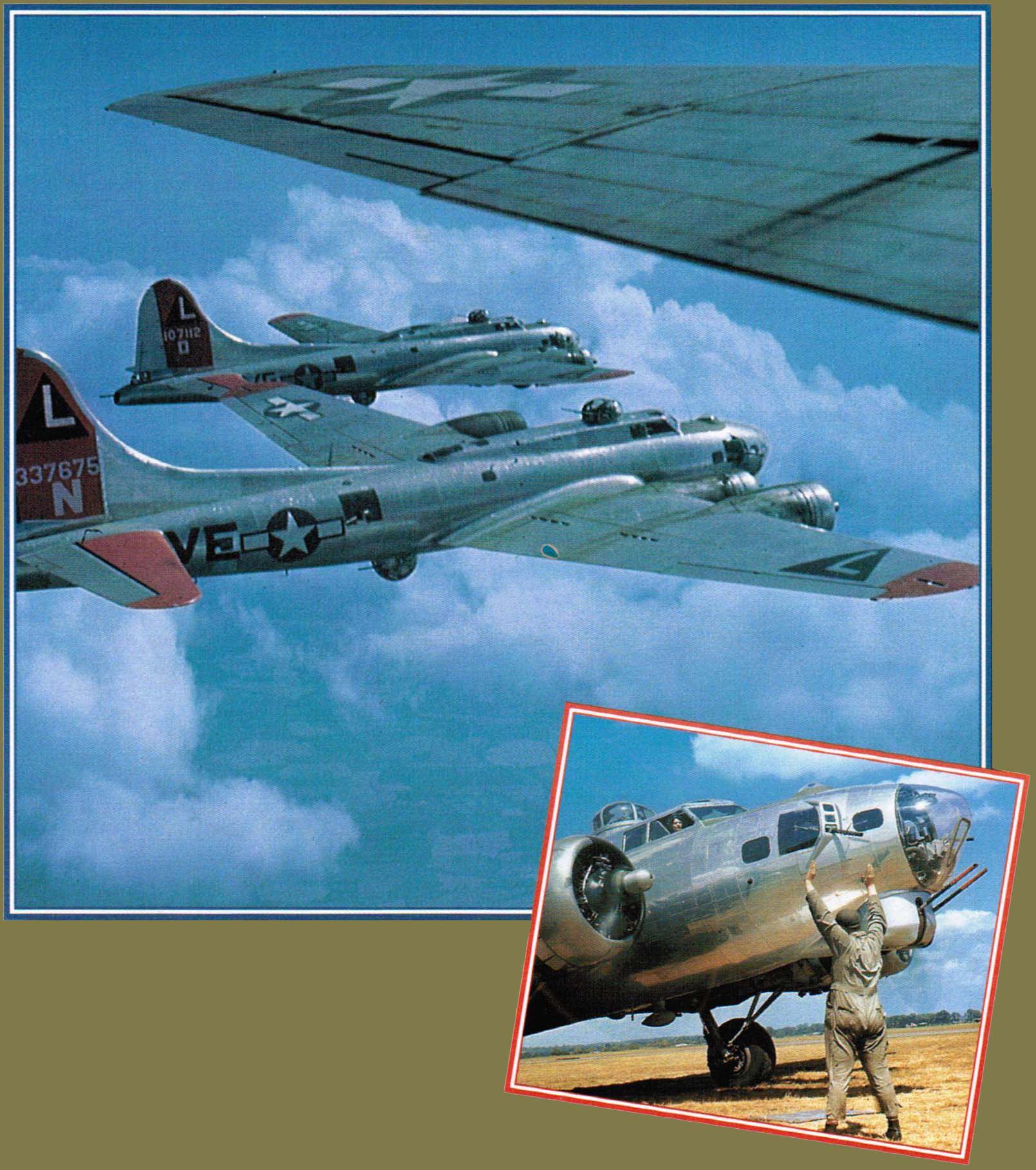

The Flying Fortress was America's main strategic weapon in Europe during World War II. From the summer of 1943, huge numbers of Boeing's great silver bird were to be found on English airfields.
Fortress in the sky
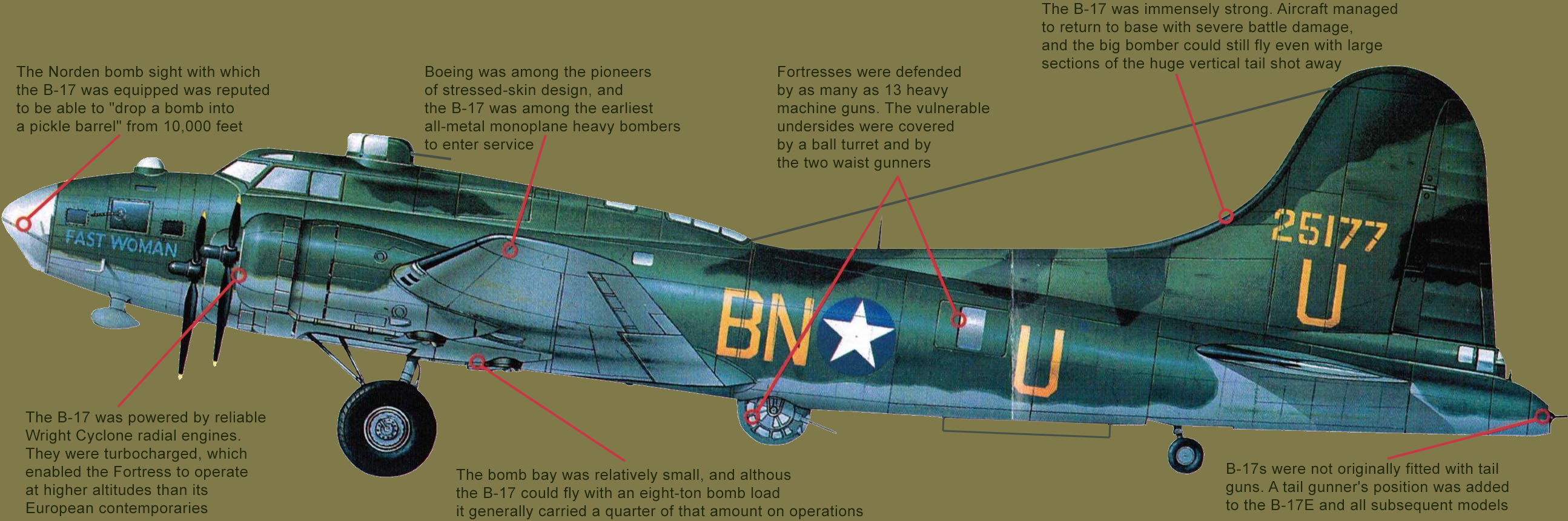
In the mid-1930s, Boeing engineers suggested a big bomber to the U.S. Army Air Corps. The best American bomber at the time was an inadequate twin-engine adaptation of the DC-3 transport. The decision to go ahead with the 15-17 Flying Fortress was a courageous leap forward: it gave the United States an embryonic strategic bomber force by the time the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor. Early B-17s did not have enough guns and were not available in sufficient numbers, but as the" war progressed the Flying Fortresses took command of the skies.
15-17 crews faced many unspeakable horrors, pressing ahead into Luftwaffe fighters and flak while blinded by smoke, slammed by turbulence, plagued with mechanical mishaps, and paralyzed by the numbing cold. On the first Berlin mission, B-17 crewmen killed in the air numbered the same as Germans killed on the ground by bombs (about 400). As the bombing campaign wore on casualties aboard the B-17s remained high, but the bombing became more effective.

Right: B-17s were used to make precision daylight attacks on German industrial centers.
Left: Hit by flak, a burning B-17 falls away from the protection of its fellows.

The "Mighty Eighth" Air Force was the premier user of the B-17 Flying Fortress.
B-17F "Fast Woman"
"Fast Woman" was one of the first American B-17s to arrive in Britain during World War II. Attached to the 359th Bomb Squadron of the 303rd Bomb Group, it was based at Molesworth in Huntingdonshire.
SPECIFICATIONS B-17G
Type: Nine/10-seat long-range bomber.
Powerplant: Four 1,200-hp. Wright R-1820-97 Cyclone turbocharged radial piston engines.
Maximum speed: 290 m.p.h. at 25,000 ft.
Ceiling: 35,600 ft.
Range: 2,000 mi. with 5,000-lb. bomb load.
Weights: Empty 37,300 lb.; loaded 65,500 lb.
Weapons: 13 .50 cal. machine guns in twin turrets, plus single dorsal and fore and aft beam positions; 17,600-lb. max bomb load.
Dimensions:
Span 103 ft. 9 in.
Length 79 ft. 9 in.
Height 19 ft. 1 in.
Wing area 1,420 sq. ft.


Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
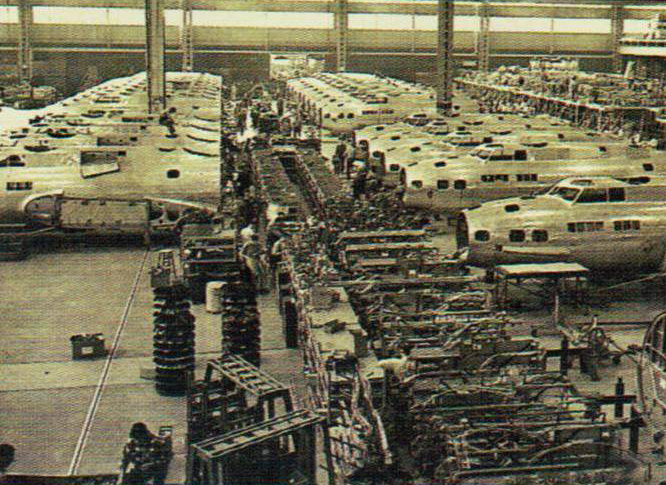

Mass production
Nowhere was America's huge industrial might more visible than in the aircraft factories that turned out hundreds of B-17s each month.
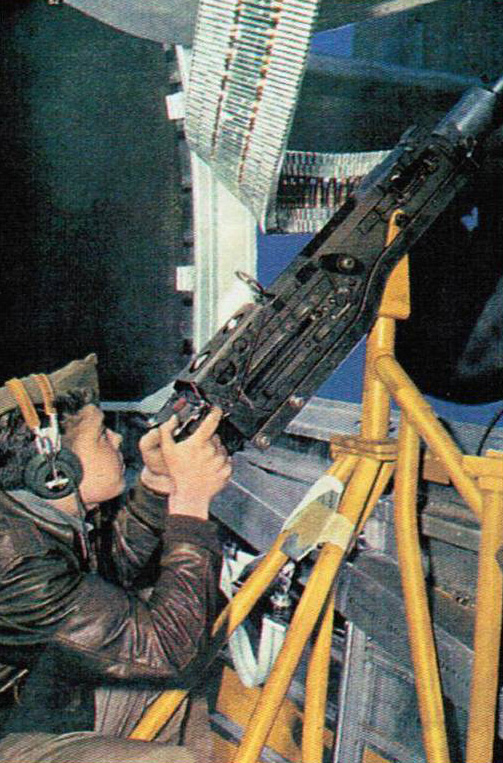

Gun platform
Key to the B-17's design was its heavy machine gun armament, designed to enable the bombers to penetrate defended airspace unescorted.
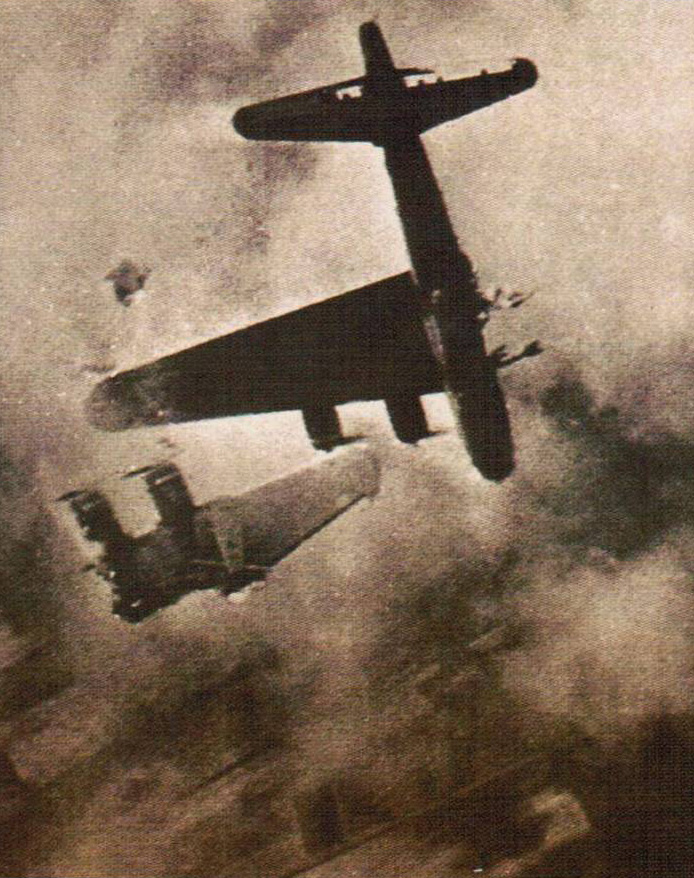

A hard-fought battle
The Fortress was tough, but over Germany it was pitted against some of the most experienced fighter pilots in the world, and losses were heavy.

The young man's war
It was a rare B-17 pilot who was older than 30. Most of the men who took the big bombers into battle were barely into their 20s.
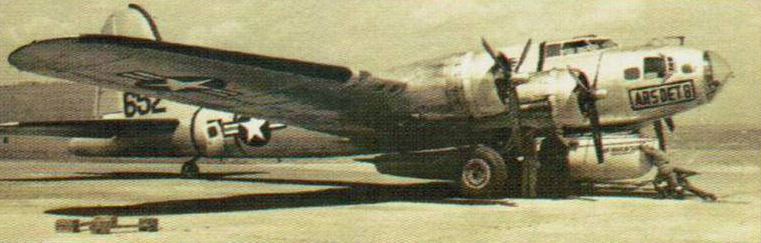
Silver machines
The B-17 soldiered on after World War II in some oddball roles. This is a rescue aircraft with a lifeboat carried under the fuselage.
FACTS AND FIGURES
▶ A B-17 shot down by Japanese Zeroes on the way to Pearl Harbor was the first American combat loss in World War II.
▶ The Boeing 299, the Flying Fortress prototype, first flew on July 28, 1935.
▶ 12,731 B-17s were built, with production of the B-17G model by Boeing, Douglas and Lockheed reaching 8,680.
▶ At the height of the war in Europe, B-17s flew from more than 25 airfields in the south and east of England.
▶ More than 47,000 U.S. 8th Air Force crew died in daylight raids over Germany.
▶ An SB-17, a Fortress converted for search and rescue duty, flew the first American sortie of the Korean War.
We have much more interesting information on this site.
Click MENU to check it out!
∎ cartalana.com© 2009-2025 ∎ mailto: cartalana@cartalana.com