
GEORGE FORTY
WORLD WAR TWO. ARMOURED FIGHTING VEHICLES & SELF-PROPELLED ARTILLERY
A small number, only twelve. 15cm siG33 auf Fahrgestell PzKpfw II (Sf) heavy infantry guns were produced in late 1941, using a specially widened and lengthened PzKpfw II chassis, measuring 18ft long, 8ft 8ins wide and 6ft 4ins high, so the vehicle was lower than the PzKpfw II except when the gun was elevated. The lengthened chassis carried an extra roadwheel on each side but was otherwise unchanged, even though the total weight was increased by over 1 ton to 11.2 tons. The superstructure had 30mm thick armour in front and 15mm on the sides. The gun had fifty degrees of elevation and twenty degrees traverse. Thirty rounds of ammunition were carried. All were deployed by the Deutsches Afrika Korps in North Africa.
In 1942, the Wehrmacht decided to develop a self-propelled version of their standard 10.5cm leFH18M field howitzer to provide fire support for their Panzer divisions. They chose the obsolescent PzKpfw II chassis, building the SdKfz 124 Leiehte Feldhaubitze 18/2 auf Fahrgestell PzKpfw II (Sf) Wespe (Wasp) as it was designated, on a slightly lengthened chassis with only three top rollers instead of four and spring loaded bumper stops for the road wheels. The superstructure armour of the 11.7 ton Wespe was 20mm thick in the front, 15mm at the sides and 8mm at the rear. The driver was seated well forward, separated from the three-man gun crew. Although 1,000 were initially ordered only 676 were eventually built, between 1943 and 1944. They first entered service about the time of the great Kursk tank battle and remained operational for the rest of the war, A further 159 munitions carriers (Munitions-Selbstfahlafette auf Fahrgestell PzKpfw II) were built and carried ninety rounds of ammunition, in support of Wespe which carried only thirty- two rounds. The vehicle measured over 16ft long, 7ft 7½ins wide and 7ft 8ins high, had a top speed of 25mph and a range of 137 miles. The gun had forty-five degrees of elevation, thirty-four degrees of traverse and a maximum range of 10675 metres.
The name Marder (Marten) was given to three self-propelled anti-tank guns during World War Two, Marder I and Marder III both mounting foreign manufactured weapons while the Marder II fitted the German 7.5cm PaK40/2 mounted on the PzKpfw II chassis. This was produced as a deliberate attempt to upgun the obsolescent PzKpfw II and of the 651 produced. only seventy-five were converted the rest being built from new between June 1942 and June 1943. The conversions followed when production was switched to building Wespe. The 10.8 ton, four-man SP had an open-topped box-like superstructure with 30mm thick armour in front and 10mm on the rest. It had a top speed of 25mph and a range of nearly 120 miles The Marder II entered service in July 1942 and continued to be used in action for the rest of the war. Its gun could penetrate 92mm of armour plate at 900 metres. Thirty-seven rounds (both AP and HE) of ammunition were carried Its German designation was SdKfz 131 7.5cm PaK40/2 auf Fahrgestell PzKpfw II (Sf) Warder II.
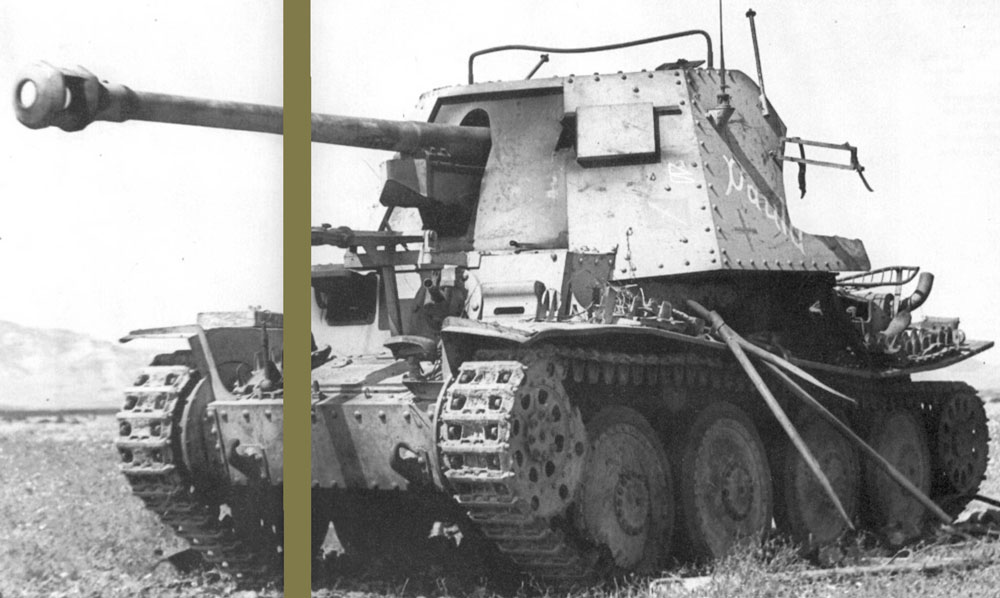

The 7.5cm PaK40/3 auf PzKpfw 38 (t) Ausf H (SdKfz 138) was a self-propelled anti-tank gun on the Czech-built chassis. Over 400 were in service (175 being converted from tanks in 1943, the rest built from new). They served in Russia, Tunisia and Italy. (TM)
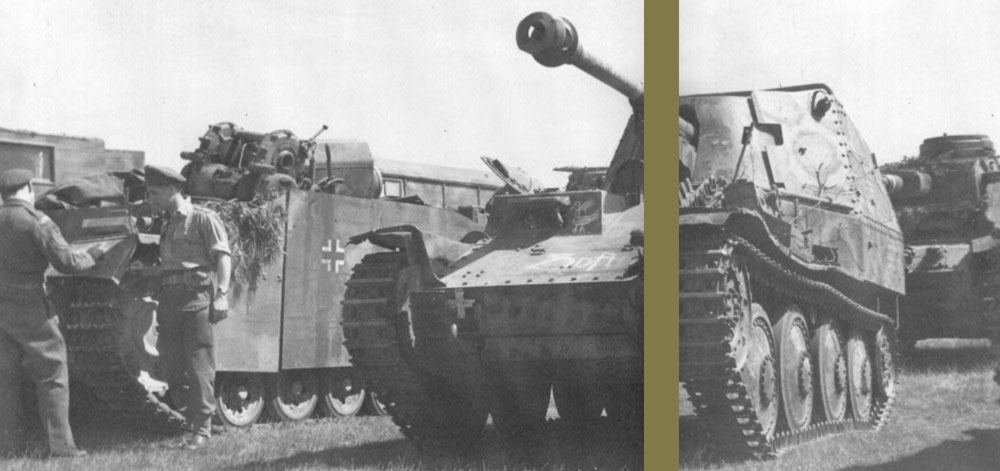
Marder III in an armoured vehicle dump, Amersfoort, Holland at the end of World War Two. Production of the Marder ended in May 1944. The Hetzer was deployed for the rest of the war. (TM)
The SdKfz 132 Panzer Selbstfahlafette I fur 7.62cm PaK 36(r) auf Fahrgestell Ptzkpfw II Ausf I) und E mounted a captured Soviet 7.62mm PaK 36 anti-tank gun, which had been fitted with a muzzle brake and re-chambered so that it could fire German PaK 40 ammunition (thirty rounds carried). A large number of these guns had been captured early in Operation Barbarossa and when firing the PaK 40 ammunition it could penetrate 80mm of armour plate at 900 metres. The SdKfz 132 weighed 11,5tons had an open-topped 15mm thick armoured superstructure which extended over the whole length of the vehicle. The gun, still fitted with the normal shield, fired over the superstructure and could traverse fifty degrees and elevated from minus five degrees to plus sixteen degrees. Approximately 200 were converted between April 1942 and June 1943.
Built in 1943 the SdKfz 140 leichte Flakpanzer 38(t) auf Selbstfahlafette 38(t) Ausf M was the very first German (ex-Czechoslavak) full-tracked vehicle to be used for an AA weapon. The gun chosen was the 2cm FlaK 38 which fired both HE and AP tracer, to an effective ceiling of 3200 metres, fed from a twenty round magazine. Rate of fire was 180-220 rounds per minute (rpm) and a total of 1040 rounds were carried. The gun had all-round traverse and could elevate to ninety degrees. One hundred and forty of these 9.8ton, 16ft 2½ins long, 7ft 1ins wide and 7ft 6ins high AA tanks were produced between late 1943 and early 1944. It had a top speed of 25mph and a range of 115 miles.
The SdKfz 139 Panerjaeger 38(t) fur 7.62cm PaK36(r) Marder III was again the simple use of an obsolescent tank chassis to mount a larger anti-tank gun, the Soviet 7.62cm PaK36 on the Czechoslovak-built TNHPS chassis (thirty ammunition rounds carried). In 1942 a total of 344 were built and later a further nineteen were converted from gun tanks. Weighing 10.6 tons, the Marder III measured 19ft 6ins long, 7ft 2½ins wide and 8ft 1in high, so it had a high silhouette and very little protection for the four-man crew. Over 2240lbs heavier than the gun tank, the vehicle had to be re-engined with the more powerful 150hp EPA-2 engine. It entered service in July 1942 and was deployed on the Eastern Front and also in North Africa.
In early summer 1942, it was decided to build a new SP gun. again based on the 38(t) chassis, but this time mounting the German 7.5cm PaK40/3 L/46 anti-tank gun instead of the Russian 7.62cm. The prototype of the SdKfz 138 7.3m PaK40/3 auf PzKpfw 38(t) Ausf H was ready in June 1942 and was fitted with an improved superstructure, giving better crew protection. With a crew of four, the 10.7 ton vehicle had a top speed of 25mph and a range of 115 miles, Its main armament could be elevated from minus five degrees to plus twenty-two degrees and traversed sixty-five degrees each side in the forward arc. Firing AFC' (forty rounds carried, plus thirty-eight HEAP) the gun could penetrate 76mm of armour at 2300 metres. Armour plate on the superstructure was 10-15mm thick and the SdKfz 138 measured just under 19ft long (including gun), 7ft wide and 8ft 3ins high. Approximately 240 were built between 1942-43. A further 175 were converted from gun tanks in 1943. They were deployed to the Eastern Front, also in Tunisia and Italy. Of those built eighteen were exported to Slovakia.
The SdKfz 138 Panerjaeger 38(t) mit 7.5cm PaK40/3 Ausf M was the largest of the early production Panerjaeger on the 38(t) chassis and was a better designed version mounting the German 7.5cm Pak40/3 L/46 gun and was also called the Marder III. It came about after Hitler had personally ordered all 38(t) production to be switched to building SPs (so a complete redesign was possible) to replace the models built to date. The major change was to move the engine to the middle of the chassis, thus enabling the gun to he mounted at the rear, making it more stable, more manoeuverable (as the gun did not overhang) and lighter (10.5tons) because the frontal armour did not need to be as thick. The resulting Marder III was built between April 1943 and May 1944. but when after 975 had been built it was replaced by the Hetzer (Baiter). It saw service on all Axis battlefronts of the war from May 1943 onwards.
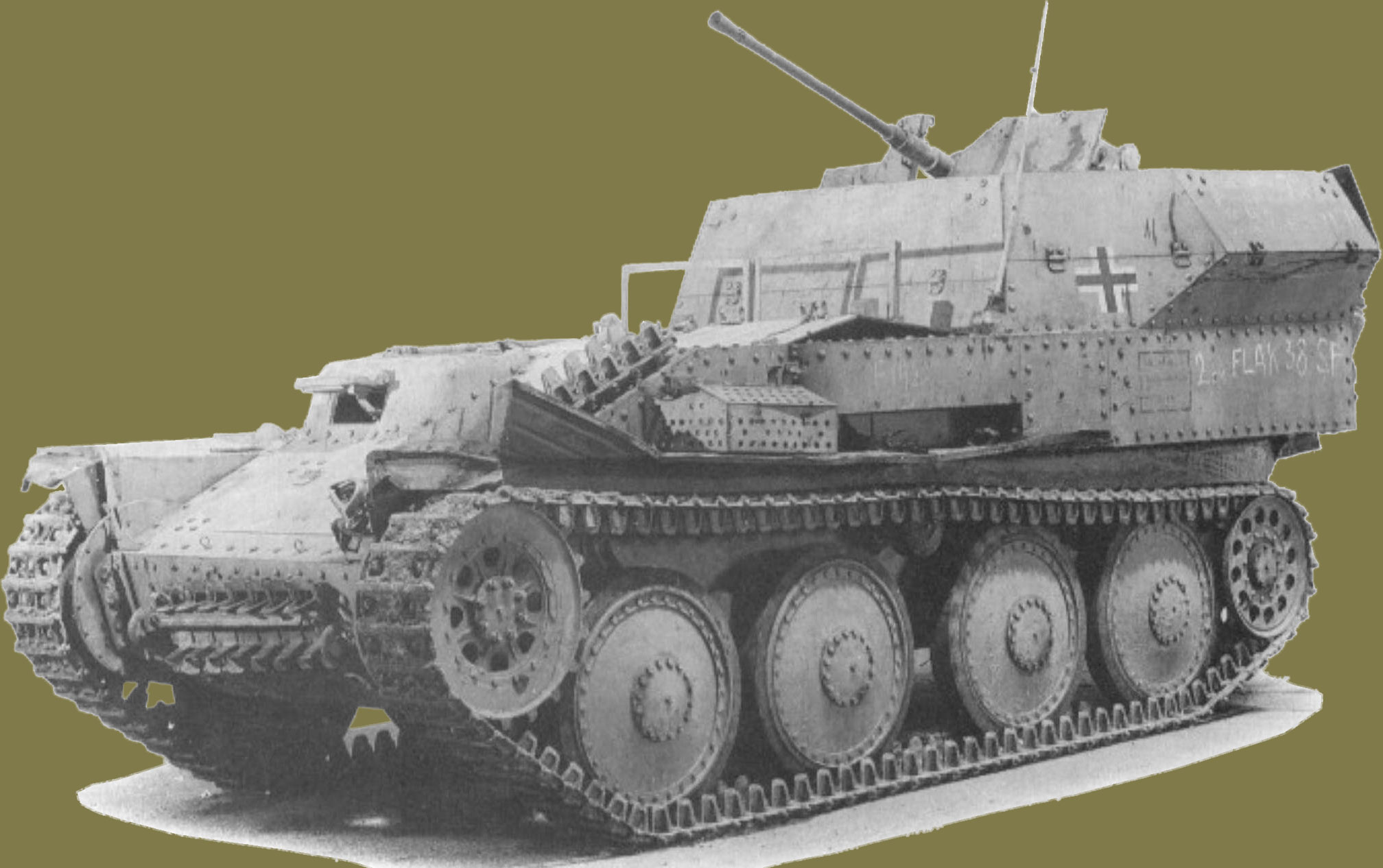
Another use of the 38(t) chassis was to mount a 2cm FlaK 38 L/112.5 AA gun, and was designated as the Flakpanzer 38 (t) auf Selbstfahlafettee 38 (t) Ausf M (SdKfz 40). (TM)
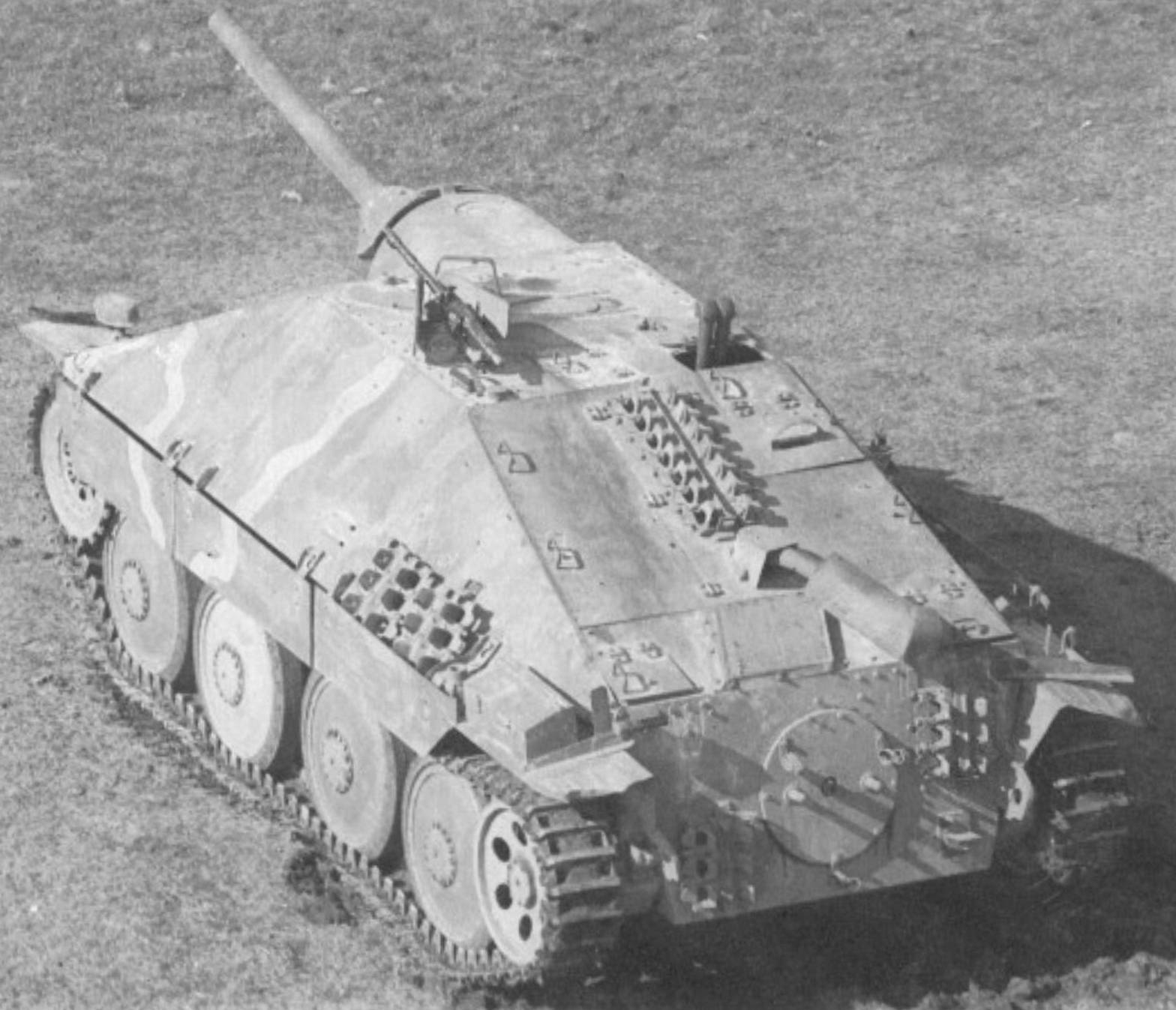

One of the best light tank destroyers, the 15.75ton Jagdpanzer 38 (t) Hetzer (Baiter) which mounted a 7.5cm PaK 39 L/48 gun in a low, streamlined chassis. (TM)
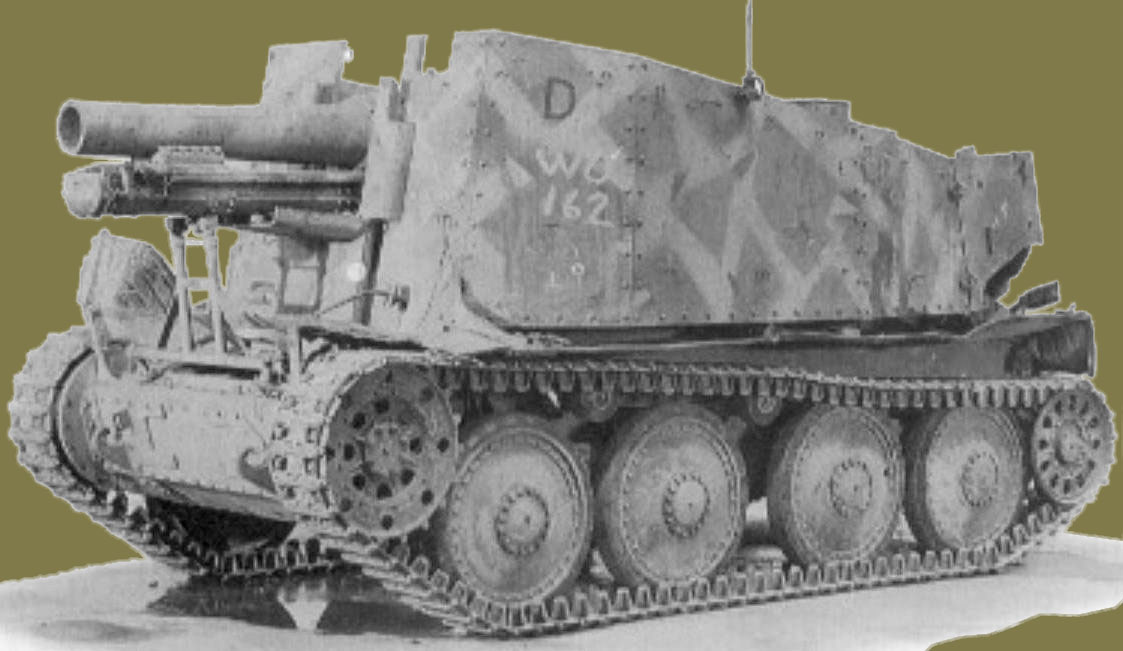
Grille (Cricket) was yet another SP infantry gun which used the excellent 38(t) - either Ausf H or M - chassis. Between 1943 and 1944 a total of 232 were built. (TM)
As the war on the Eastern Front progressed, it became clear that there was a need for a light tank destroyer (Jagdpanzer) to replace the existing both towed and self-propelled light anti-tank guns. Indeed, General Heinz Guderian, Inspector of Armoured Units, was calling for one to be designed as early as spring 1943. Development was centered upon a widened TNHP chassis, as the running gear of Hetzer was about ten percent larger, with a track width of some 1ft 2ins as it had to carry the extra 5 tons weight of the heavily armoured bodyshell - armour was 20 to 60mm thick. When built the Jagdpanzer 38(t) Hetzer was 15.8 tons in weight, 21ft 3½ins long (including gun), 8ft 9ins wide and 7ft 2½ins high. The gun was a 7.5cm PaK39 L/48 which was offset to the right in the slop ing front plate, the driver seated to its left and the rest of the four-man crew in the fighting compartment. Traverse was only five degree left and eleven degrees right, so the vehicle had to track to engage targets. Forty-one rounds were carried in the vehicle. An MG 34 or MG 42 was mounted on the roof and remotely controlled from inside the vehicle. Hetzer had a top speed of 24mph and a range of 110 miles, it first entered service in July 1944 and fought for the rest of the war. After the war it was used by both the Czecholsovak and Swiss armies. From April 1944 onwards 2.584 were produced.
Two adaptations of Hetzer were built, the Flammpanzer 38(t) Hetzer, twenty being converted by fitting a 14mm Flammenwerfer in place of the 7.5cm anti-tank gun and the Bergepanzer 38(t) Hetzer armoured recovery vehicle, sixty four being converted to this role. With the gun removed and a winch fitted in the lighting compartment, it was deployed in tank hunting units equipped with Hetzer.
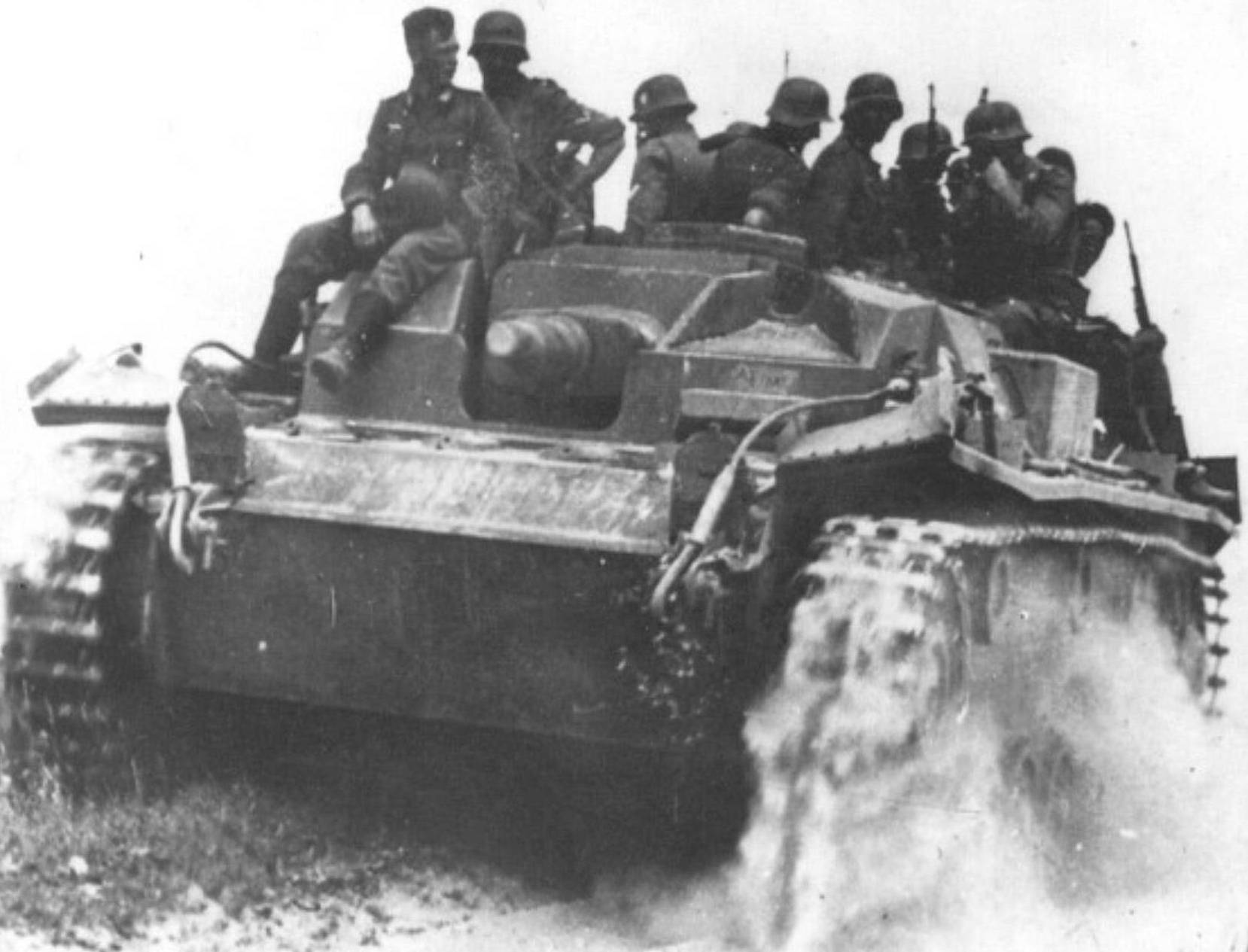

Stug III Ausf A/B assault gun mounting a 7.5cm StuK 37 L/24 gun. This one is carrying Panzergrenadiers into action. (TM)
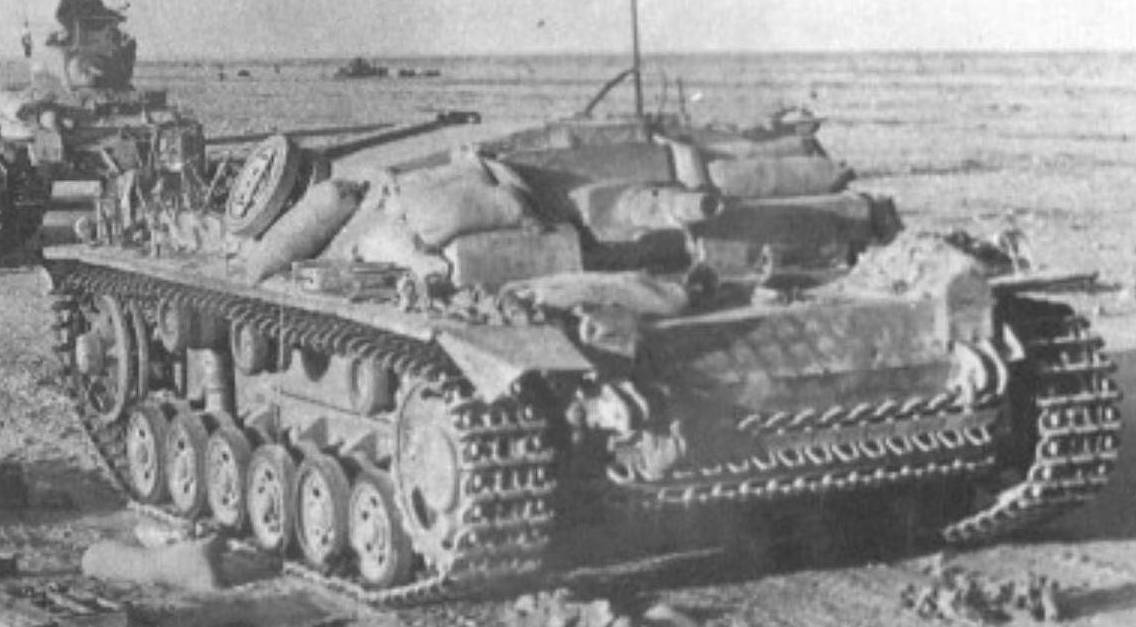

The Stug III Ausf C/D did not have the gunner's direct vision port and improved armour. (TM)
The SdKfz 138/1 15cm schwerer Infanteriegeschütz 33(Sf) auf PzKpfw 38(t) Ausf H Grille (Cricket) carried a 15cm siG33/l L/12 heavy infantry gun mounted on the rear-engined 38(t) Ausf H chassis (as Sd Kfz 138). Ninety of these 11.5tonners were produced during early 1943, .dl had a crew of five and a top speed of 22mph. Issued to Panzergrenadier regiments from early 1943, it saw service in all European and other battle areas. Eighteen rounds of ammunition were carried for the 15cm gun which had seventy-three degrees of elevation and ten degrees of traverse on its mount and a maximum range of 4,700metres. It was followed by a second type of Sd Kfz 138/1 Grille, which used the Ausf M chassis. A further 282 were built of this slightly heavier type (12tons) the 15cm schwerer Infanteriegeschütz 33/1 auf Selbstfahrlafette 38(t) (Sf) Ausf M, which like its predecessors saw service on all fronts for the rest of the war.
Munitionspanzer 38(t) (Selbstfahrlafette) Ausf M was the tracked ammunition carrier needed to back up Grille which had a small ammunition carrying capacity. The plan was to have two of these with each detachment of six Grille as they could each carry forty rounds of 15cm ammunition. Between January and May 1944 a total of 102 were built.
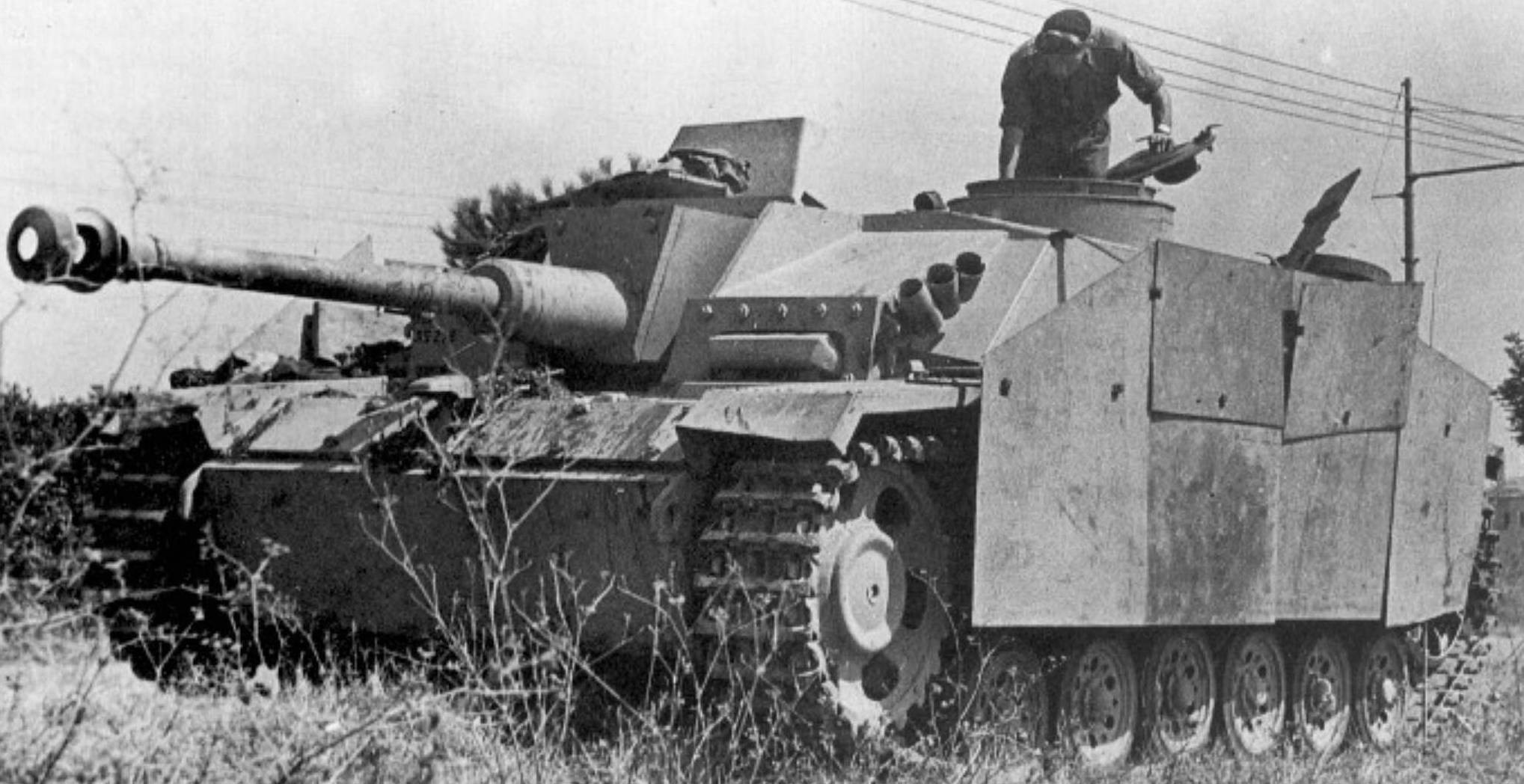

Last model of the Stug III was the Ausf G which had better vision devices for the commander and a shield for the MG 34 located by the loader's hatch. Over 7,700 were built, far more than any other model. (TM)
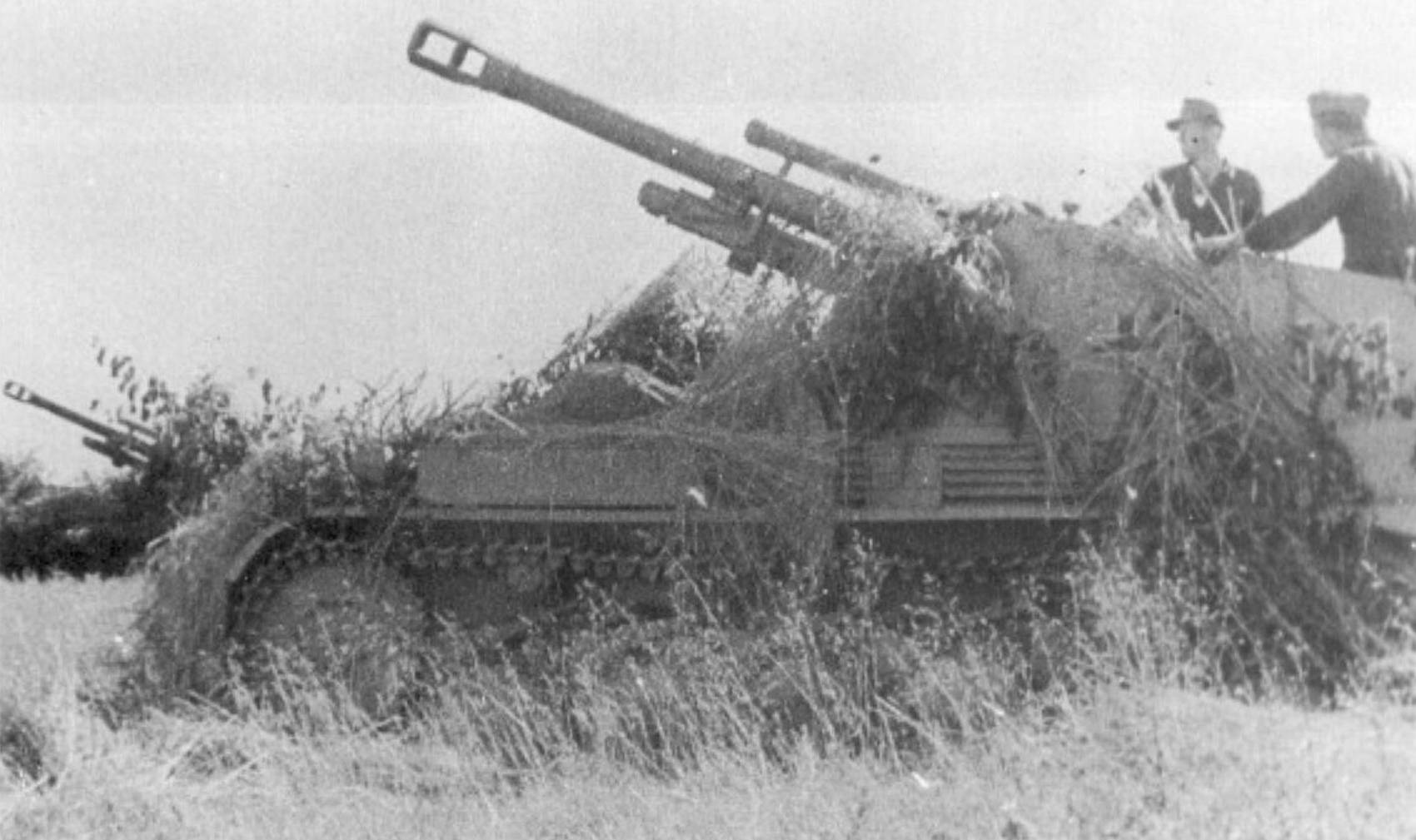

The most well-known SP on the Pzkpfw II chassis was the SdKfz 124, Wespe (Wasp) which mounted a 10.5cm howitzer. These were photographed in Russia, 1943. (GF)
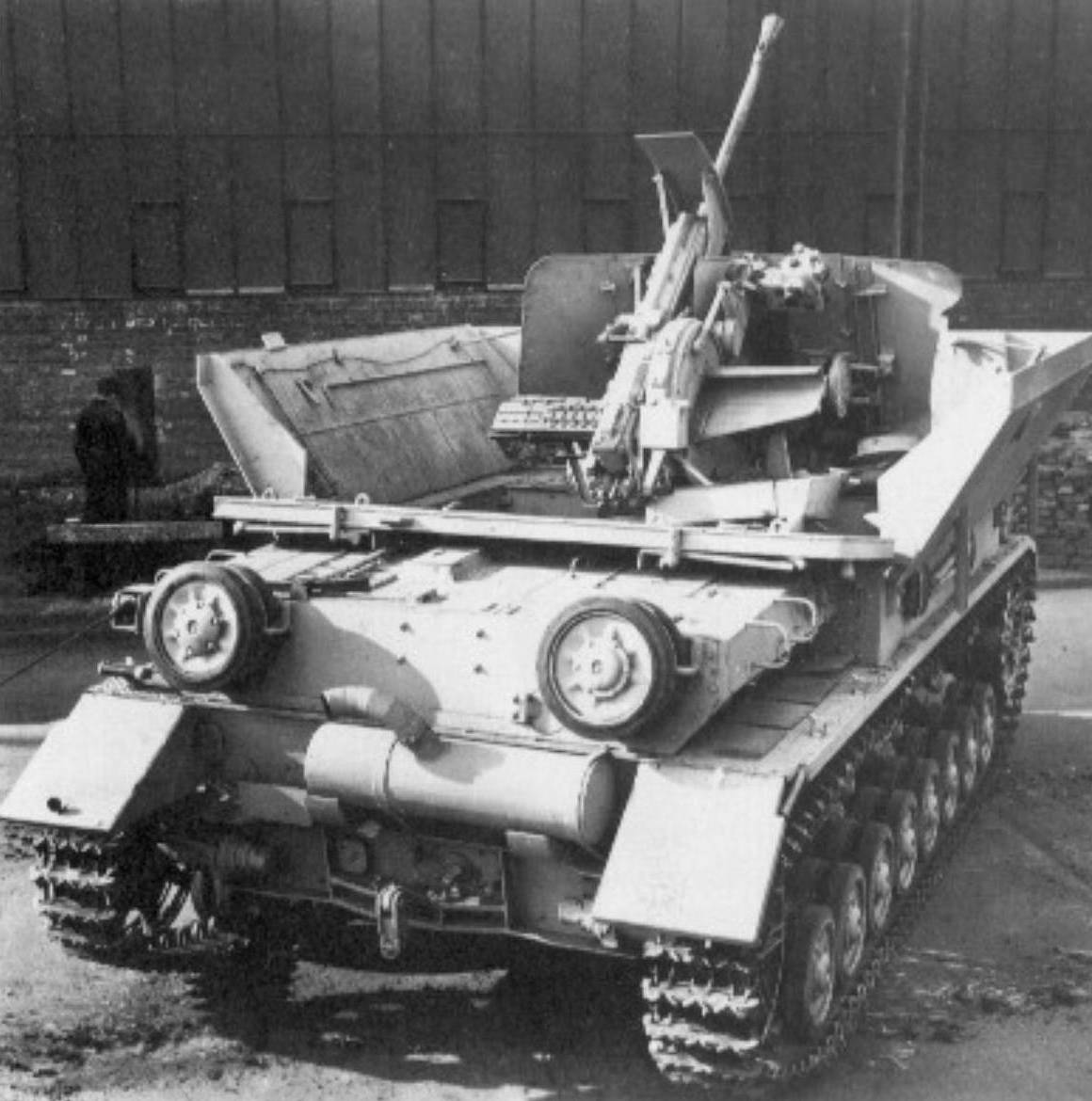

The 3.7cm FlaK auf Fahrgestell PzKpfw IV was also called Möbelwagen (Furniture Van) and was designed to give Panzer units AA protection. (TM)
As early as 1936 it was decided that Panzer divisions needed mobile assault and anti-tank guns Sturmgeschütz (StuG) of at least 7.5cm calibre. The PzKpfw III light/medium tank chassis was chosen as the basis, but mounting the low velocity 7.5cm gun of the PzKpfw IV. Later, higher velocity guns were mounted which made it possible to achieve both the assault gun and the self-propelled anti-tank gun roles. From the outset the StuG was designed as a dual purpose weapon system. The StuG Ausf A (Sd Kfz 142) was the first to be produced in early 1940 and was followed by the Ausf B, Ausf C und D, and Ausf E, all being armed with the short-barrelled 7.5cm StuK37 L/24 gun. The Ausf F entered service mounting the long-barrelled 7.5cm StuK40 L/43 or L/48, making it a lethal ami tank weapon as well as an assault gun. This type (allotted a different Sonderkraftfahrzeug (SdKfz) special purpose vehicle number SdKfz 142/1) continued through Ausf F/8, Ausf G then onto the StuH42 (Sd Kfz 142/2), which mounted the more powerful 10.5cm gun. There were also a lew flamethrowers (StuG III), assault guns (StuG 33B) and ammunition carriers. Approximately 680 of the early type of StuG III were built, over 8,500 of the dual purpose StuG III and over 1,210 of the Sturmhaubitze 42 (StuH42). The largest build of the series was that of the Ausf G, 7720 being built and a further 170 plus converted from gun tanks. Tank aces, such as Michael Wittmann, learned his skills commanding one of the first StuG Ills to be allocated to the Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler, knocking out many enemy tanks on the Eastern Front.
| Specifications | StuG III Ausf A | StuG III Ausf F | StuH42 |
| Weight (tons) | 19.6 | 21.6 | 24 |
| Crew | four | four | four |
| Dimensions: | |||
| Length | 17ft 11ins | 21ft | 20ft 5½ins |
| Width | 9ft 8½ins | 9ft 8½ins | 9ft 8½ins |
| Height | 6ft 6ins | 7ft 2ins | 7ft 2¾ins |
| Armament | 7.5cm StuK 37 L/24 | 7.5cm StuK 40 L/43 or L/48 | 10.5cm StuH 42 L/28 and one MG 34 or MG 42 |
| Armour up to 50mm up to 80mm with Saukopf *a | |||
| Engine Maybach HL 120TR | Maybach HL 120TRM | ||
| Top speed all 25mph | |||
| Range | 100miles | 100miles | 97miles |
| a. this was a large cast gun mantlet, nicknamed by crew's Saukapf (pig's head) because of its shape | |||
As with the PzKpfw III chassis, the ubquituous PzKpfw IV was also used as the mount for a wide variety of guns, including anti-tank, infantry assault, self-propelled artillery and anti-aircraft. In the first of these categories there were five main Panzerjaeger, which are summarised in the following table:
| Name | Armament |
| StuG IV | 7.5cm StuK 40 L/48 |
| Jgd Pz IV | 7.5cm PaK 39 L/48 |
| Pz IV/70 (V) | 7.5cm PaK 42 L/70 |
| Pz IV/70 (A) | 7.5cm PaK 42 L/70 |
| Nashorn (Rhino) | 8.8cm PaK 43/1 L/71 |
| PaK: Panzer abwher Kanone (anti-tank gun) | |
The first of these, the StuG IV came into being as a result of heavy bombing halting StuG III production at the Alkett works. Also Hitler ordering that PzKpfw IV production should be stopped so that Krupp could instead manufacture StuG IVs. They produced their first vehicle in December 1943 and it proved to be an excellent assault gun or tank destroyer, weighing 23 tons with a top speed of just under 24mph and a range of 130 miles.
The very similar, but slightly more streamlined Jagdpanzer IV was produced by Vomag as a successor to the StuG III and was first issued to Panzerjaeger units in March 1944, seeing service in Russia and later in Normandy. Weighing over 2240lbs heavier than the StuG IV, it had approximately the same performance but its frontal armour was only 60mm instead of 80mm thick. The two PzKpfw IV/70(V) & (A) were built as improved models of Jagdpanzer IV, both mounting the long-barrelled version of the 7.5cm anti-tank gun. The (A) - Alkett version was 2 tons heavier at 28 tons (thicker armour on the lower hull), but they were otherwise very similar in appearance. The (V) Vomag version Nashorn (Rhino), on the other hand was entirely different to the other four, being built to provide a suitable SP version of the 8.8cm PaK43 gun. It used the same basic chassis as the Hummel (Bumble Bee) and proved to be a highly effective tank killer, with a top speed of 26mph and a range of 135 miles.
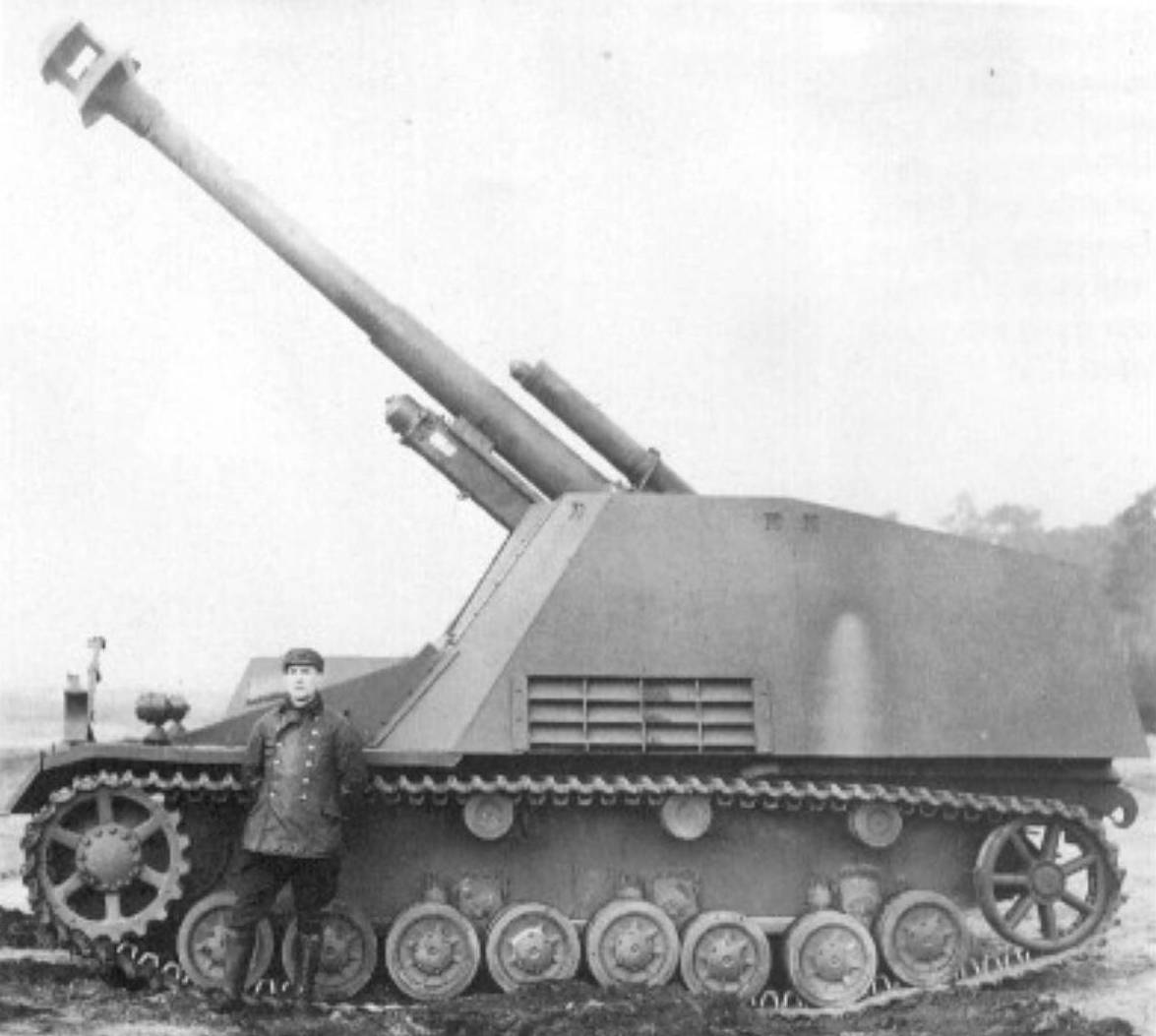

Hummel (Bumble Bee) was a 15cm heavy howitzer on the PzKpfw IV chassis. This is the prototype vehicle built by Alkett. (TM)
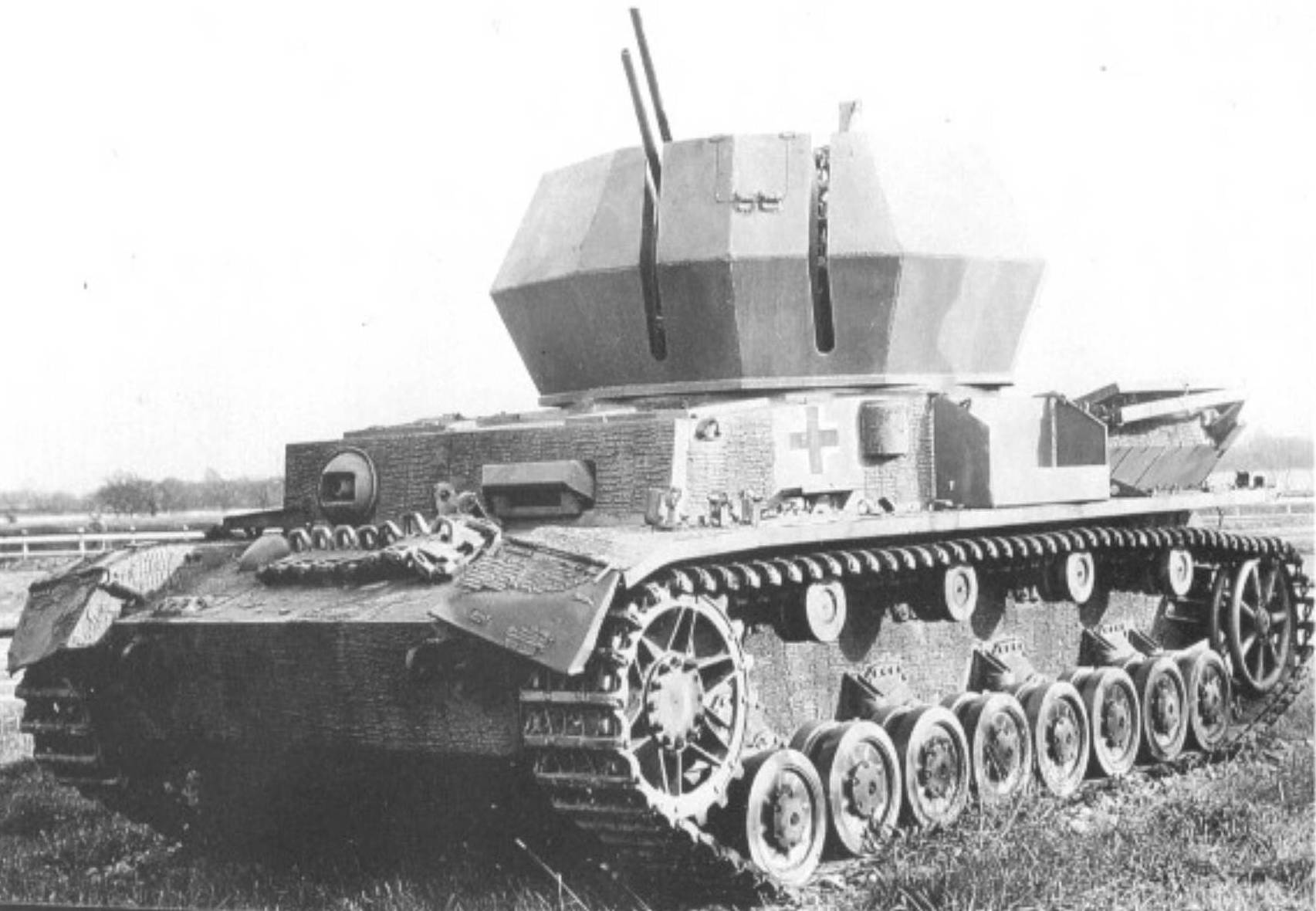

Wirbelwind (Whirlwind) mounted the four-barrelled 2cm FlaKvierling in an open-topped fully-traversing turret. Only two of the four guns are fitted. (TM)
We have much more interesting information on this site.
Click MENU to check it out!
∎ cartalana.com© 2009-2025 ∎ mailto: cartalana@cartalana.com